更多答案也可以关注我的GitHub算法仓库——Algorithm
(大家可以根据我每道题打的星来衡量这道题的难易,星越少越难)
基础数据结构:
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}8.字符串转换整数 (atoi)
自动机
我的代码就是根据题意一步一步判断的,所以非常臃肿,但是根据官方给的自动机解法暂时还没看懂
public int myAtoi(String s) {
int j = 0;
for (; j < s.length();) {
if (s.charAt(j) == ' ') {
j++;
}else {
break;
}
}
s = s.substring(j);
if (s.length() <= 0) {
return 0;
}
boolean isNegative = false;
int i = 0, res = 0;
if (s.charAt(0) == '-' || s.charAt(0) == '+') {
if (s.charAt(0) == '-') {
isNegative = true;
}
i = 1;
}
for (; i < s.length();) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '0') {
i++;
}else {
break;
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
for (; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9') {
sb.append(s.charAt(i));
}else {
break;
}
}
String str = sb.toString();
if (str.length() != 0) {
if (str.length() > 10) {
if (isNegative) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}else {
long l = Long.valueOf(str);
if (l > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
if (isNegative) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}else {
if (isNegative) {
return -1*Integer.valueOf(str);
}
return Integer.valueOf(str);
}
}
}
return res;
}2.两数相加
话说真快被链表题搞懵了呀,这个我也是按照纯模拟加法的思路写的,先去判断哪个链表长,然后哦就把短的依次加到长的上面,还要注意进位问题。
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode cul1 = l1;
ListNode cul2 = l2;
int l1_len = 0;
int l2_len = 0;
while (cul1 != null || cul2 != null) {
if (cul1 != null) {
l1_len++;
cul1 = cul1.next;
}
if (cul2 != null) {
l2_len++;
cul2 = cul2.next;
}
}
ListNode lon = l1;
ListNode shor = l2;
if (l2_len > l1_len) {
lon = l2;
shor = l1;
}
int yu = 0;
while (shor != null) {
lon.val += (shor.val+yu);
if (lon.val >= 10) {
yu = 1;
lon.val -=10;
}else {
yu = 0;
}
shor = shor.next;
if (lon.next == null && yu == 1) {
lon.next = new ListNode(0);
}
lon = lon.next;
}
while (yu == 1) {
lon.val += 1;
if (lon.val >= 10) {
yu = 1;
lon.val -= 10;
if (lon.next == null) {
lon.next = new ListNode(0);
}
lon = lon.next;
}else {
yu = 0;
}
}
if (l2_len > l1_len) {
return l2;
}
return l1;
}82.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
判断当前节点的下一个节点与下下一个节点的值,相等则不断调整当前节点的next,不相等则向后移动;这里引入头节点方便对首元节点的操作。
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode fake = new ListNode();
fake.next = head;
ListNode cur = fake;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
int x = cur.next.val;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == x) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return fake.next;
}144.二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return list;
}
public void dfs (TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
list.add(root.val);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
}148.排序链表
这道题思路是归并,但是有两个归并思路:
- 递归着归并,先找中点(使用快慢指针),一次分一半,递归,一次分一半,递归....然后两两合并并返回
- 先设归并长度为1,第一波归并完再把归并长度乘2,再归并,以此类推
(本体采用自顶向下的递归方式)
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return sort(head, null);
}
private ListNode sort(ListNode start, ListNode end) {
if (start == end) {
return start;
}
ListNode fast = start, slow = start;
while (fast != end && fast.next != end) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode l2 = sort(slow.next, end);
slow.next = null;
ListNode l1 = sort(start, slow);
return mergeTwoLists(l1, l2);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) {
return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
}else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l2.next, l1);
return l2;
}
}
}31.下一个排列
- 倒着遍历第一次找到第一个值变小的,记录坐标为i
- 倒着遍历第二次找到刚好比nums[i]大的坐标j
- 交换i,j并翻转i+1到结尾的数字
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int i = nums.length - 2;
while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i+1]) {
i--;
}
if (i >= 0) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (j > i && nums[j] <= nums[i]) {
j--;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
}
for (int x = i+1, y = nums.length-1; x < y;) {
swap(nums, x, y);
x++;
y--;
}
}
private void swap (int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int swap = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = swap;
}
}76.最小覆盖子串
思路:滑动窗口(左右指针l,r),用两个常量数组判断当前字符串是否包含模式串('a'~'Z'可以用长度60存下)
- 不包含,r++;包含,l++,并更新结果
(这道题虽然是困难,但是思路还是比较容易懂的)
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
String res = "";
int[] sarr = new int[60];
int[] tarr = new int[60];
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
tarr[t.charAt(i) - 'A']++;
}
int l = 0, r = 0;
while (l <= r) {
boolean isHave = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 60; j++) {
if (sarr[j] < tarr[j]) {
isHave = false;
break;
}
}
if (isHave) {
String temp = s.substring(l, r);
if (res.length() == 0) {
res = temp;
}else {
res = temp.length() < res.length() ? temp:res;
}
sarr[s.charAt(l) - 'A']--;
l++;
}else if (r < s.length()) {
sarr[s.charAt(r) - 'A']++;
r++;
}else {
break;
}
}
return res;
}151.翻转字符串里的单词
常规字符串算法题,比较简单,借助java的trim()和split()函数,使用StringBuilder快速追加
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
s = s.trim();
String[] arr = s.split(" ");
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (arr[i].length() != 0) {
sb.append(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
sb.append(arr[0]);
return sb.toString();
}72. 编辑距离
这里提供了两种方法:自底向上的递归和自顶向下的动规,但是递归会超时,动规就是记录了子问题的结果避免重复计算。
dp[i][j]的意思是word1.subString(0, i)变为word2.subString(0, j)所需的步数- 根据题目中给的三种操作我们可以推出核心的动态转移方程为:
dp[i+1][j+1] = 1 + Math.min(Math.min(dp[i][j+1], dp[i+1][j]), dp[i][j]);
这里由于下标从1开始到length,避免数组越界所以使下一个用当前的值
这是一道经典的动态规划题目,值得反复练习
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int l1 = word1.length();
int l2 = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[l1 + 1][l2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < l1 + 1; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < l2 + 1; i++) {
dp[0][i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < l1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < l2; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i+1][j+1] = dp[i][j]; //一样则无需多余操作步数
}else {
dp[i+1][j+1] = 1 + Math.min(Math.min(dp[i][j+1], dp[i+1][j]), dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[l1][l2];
}
//递归(超时)
public int minDistance_recursion(String word1, String word2) {
if (word1.length() == 0 || word2.length() == 0) {
return Math.max(word1.length(), word2.length());
}
if (word1.charAt(word1.length()-1) == word2.charAt(word2.length()-1)) {
return minDistance_recursion(word1.substring(0, word1.length()-1),
word2.substring(0, word2.length()-1));
}
return 1 + Math.min(Math.min(minDistance_recursion(word1, word2.substring(0, word2.length()-1)),
minDistance_recursion(word1.substring(0, word1.length()-1), word2)),
minDistance_recursion(word1.substring(0, word1.length()-1),word2.substring(0, word2.length()-1)));
}
}4.寻找两个正序数组的中位数
这道题目有两个思路:
- 合并两个有序数组,再直接输出中位数,时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(m+n)
- 划分数组+推导,时间复杂度O(logmin(m,n))),空间复杂度O(1),但是这个暂时还没搞懂
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int l1 = nums1.length;
int l2 = nums2.length;
int l3 = l1+l2;
int[] arr = new int[l3];
for (int i = 0; i < l1; i++) {
arr[i] = nums1[i];
}
merge(arr, l1, nums2, l2);
if (l3 % 2 == 1) {
return arr[l3/2];
}
return ((float)(arr[l3/2-1]+arr[l3/2]))/2;
}
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int n1 = m -1;
int n2 = n -1;
while (n2 >= 0) {
if (n1 >= 0 && nums1[n1] >= nums2[n2]) {
nums1[n1+n2+1] = nums1[n1];
n1--;
}else {
nums1[n1+n2+1] = nums2[n2];
n2--;
}
}
}
}129.求根节点到叶节点数字之和
深度优先搜索,使用StringBuilder记录路径上节点的值,再判断左右孩子为空时,将其转换成Integer。递归返回前去除 StringBuilder的最后一个字符
class Solution {
private StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
private int res = 0;
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
sb.append(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
res += Integer.valueOf(sb.toString());
}else {
sumNumbers(root.left);
sumNumbers(root.right);
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
}
return res;
}
}104.二叉树的最大深度
二叉树必需掌握的题,数据结构教材上的原题
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
前序遍历和中序遍历的概念这里就不说了,其实推的时候很容易发现是一个递归的过程,有关于递归下标的计算如图:
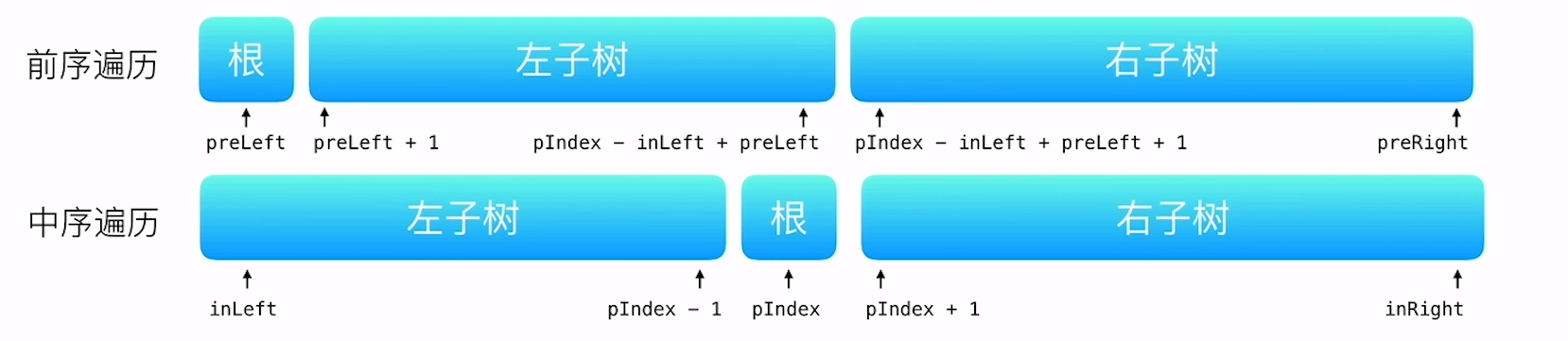
class Solution {
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return buildTree(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight) {
if (preLeft > preRight || inLeft > inRight) {
return null;
}
int val = preorder[preLeft];
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
int pIndex = map.get(val);
node.left = buildTree(preorder, preLeft+1, pIndex - inLeft + preLeft, inLeft, pIndex - 1);
node.right = buildTree(preorder, pIndex - inLeft + preLeft + 1, preRight, pIndex + 1, inRight);
return node;
}
}239.滑动窗口最大值
这道题一开始很容易想到使用优先队列来解决,但是写完检测却发现超时了,看题解是使用的单调队列(递增、递减的队列)
- 定义一个双端队列,存储数组下标,那么队首的值就是nums[queue.peekFirst()],存下标主要就是为了方便判断队列队首元素是否已经在滑动窗口外:
queue.peekFirst() < left,队首元素对应数组值最大,依次递减。 - 定义右指针
right从 0 到nums.length()-1,就很容易计算窗口的左指针left为right - k + 1 - 如果一个元素入队(入队都是从队尾入),则说明它在窗口内,那么队列内比该值小的则永远不会加入到最终答案res内,直到该元素出窗口,所以我们把队列内比该元素小的值出队。保证队列的一个单调递减。
- 最后一个
right + 1 >= k是因为这时最初的窗口才刚刚形成,满足长度为k,才能添加。
class Solution {
//单调队列
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] res = new int[nums.length-k+1];
ArrayDeque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
for (int right = 0; right < nums.length; right++) {
while (queue.size() > 0 && nums[right] > nums[queue.peekLast()]) {
queue.pollLast();
}
queue.offerLast(right);
int left = right - k + 1;
if (left > queue.peekFirst()) {
queue.pollFirst();
}
if (right + 1 >= k) {
res[left] = nums[queue.peekFirst()];
}
}
return res;
}
//优先队列(超时)
public int[] maxSlidingWindow_PriorityQueue(int[] nums, int k) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)-> b-a);
int[] res = new int[nums.length-k+1];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
queue.offer(nums[i]);
}
res[0] = queue.peek();
for (int i = k, j = 0; i < nums.length; i++,j++) {
queue.offer(nums[i]);
queue.remove(nums[j]);
res[j+1] = queue.peek();
}
return res;
}
}93.复原 IP 地址
一个字符串,分成四部分,我就懒省事直接暴力dfs了,枚举出来所有分割情况再做判断
class Solution {
private List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
private String param;
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
param = s;
dfs("", 0, 1);
return res;
}
public void dfs (String s, int index, int count) {
if (count >= 4) {
if (judge(index, param.length())) {
res.add(s + param.substring(index));
}
}else {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
if ((index + i) <= param.length() && judge(index, index+i)) {
dfs(s+param.substring(index, index+i)+".", index+i, count + 1);
}
}
}
}
public boolean judge (int start, int end) {
String temp = param.substring(start, end);
if (temp.length() <= 3 && temp.length() != 0) {
int val = Integer.valueOf(temp);
if (String.valueOf(val).length() == temp.length() && val <= 255) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}113.路径总和 II
这道题和前面的 129.求根节点到叶节点数字之和 基本一致,都是dfs+回溯即可
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>();
private int sum = 0;
private int target = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
target = targetSum;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
public void dfs (TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
sum += root.val;
cur.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (sum == target) {
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < cur.size(); i++) {
temp.add(cur.get(i));
}
res.add(temp);
}
}else {
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
sum -= root.val;
cur.remove(cur.size()-1);
}
}
}110.平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树的定义本身就是一个递归的定义:左右子树深度只差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右子树也是平衡的
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);
}
return true;
}
public int height (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
return Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
}1143.最长公共子序列
典型的二维动规,dp[i][j]代表text[0...i]和text[0...j]的最长公共子序列,所以可以推导出动态转移方程为:
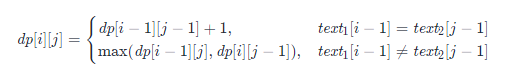
其实到这里我们可以发现有关于两个字符串之间的动态规划题目,基本都是一个二维数组dp,两个for循环里面一个状态转移方程,更新数组,最后返回数组的最后一个值,这就是动规模板。
class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int[][] dp = new int[text1.length()+1][text2.length()+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= text1.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= text2.length(); j++) {
if (text1.charAt(i-1) == text2.charAt(j-1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j]);
}
}
}
return dp[text1.length()][text2.length()];
}
}470.用 Rand7() 实现 Rand10()
古典概型
- 第一次rand7限定[1,2],判断奇偶性,概率是1/2,其实first的作用就是生成概率为1/2的奇偶。
(我们还可以通过限定[1,3],再取模3进行概率为1/3的操作) - 第二次rand7限定[1,5],概率是1/5,加上5为[6,10],概率也是1/5
- 二者结合可以得出10种概率相同的结果
借助这个思路我们也可以构造出其他的
/**
* The rand7() API is already defined in the parent class SolBase.
* public int rand7();
* @return a random integer in the range 1 to 7
*/
class Solution extends SolBase {
public int rand10() {
int first,second;
while ((first = rand7()) > 2);
while ((second = rand7()) > 5);
return first%2 == 0 ? second : second+5;
}
}543.二叉树的直径
这道题跟计算二叉树的深度还不太一样,是求任意两个节点的最大路径,可以不过根节点。递归的同时对结果更新要注意:
class Solution {
private int res = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
height(root);
return res-1;
}
public int height (TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
int l = height(root.left);
int r = height(root.right);
res = Math.max(res, l+r+1);
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}
return 0;
}
}